Effects of Quercetin on Brain Architecture in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation in Mice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26538/tjdr/v2i6.1Keywords:
Brain, Quercetin, Feulgen stain, Silver stain, NeuroinflammationAbstract
Purpose: Neuroinflammation is associated with oxidative stress, thereby leading to neuronal dysfunctions in the central nervous system. Quercetin is a well-known potent anti-oxidant capable of reducing the generation of free radicals. Preventing the generation of free radical may be a valuable therapeutic approach in the management of disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, multiples sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease associated with neuroinflammation. This work was therefore designed to investigate the effect of quercetin on brain architecture in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced neuroinflammation in mice.
Method: Fifteen (15) animals (mice) were randomly divided into a group of three consisting of five animals in each group. Neuroinflammation was induced by a single injection of 2 mg/kg Escherichia coli bacterial lipopolysaccharide (serotype 055:B5, Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA) dissolved in 0.9% sterile saline intra-peritonially (IP).
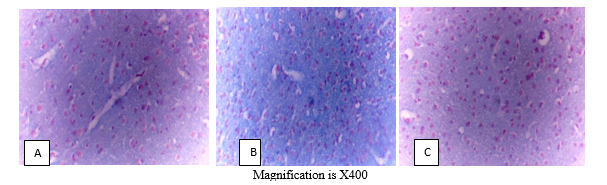
Group A served as the control group and was administered distilled water for a period of three days while group B received only LPS meanwhile group C was induced and treated with quercetin (40 mg/kg p.o) for three days. After three days, all animals were sacrificed, and their brain tissues were carefully collected for analysis. Dendritic arborization and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) were quantified using silver stain and feulgen stain respectively
Results: Silver stain revealed that quercetin in group C prevented axonal loss as compared to untreated group B. Meanwhile in the feulgen stain, the DNA was preserved by quercetin as compared to untreated group B.
Conclusion: This study has clearly revealed that quercetin prevented neuronal dysfunction during neuroinflammation through mechanisms that may involve preventing axonal and DNA loss.
Downloads
References
1. Gaber EB, Amany MB, Muhammad I, Zohair SM, Mohamed EA, Ayman ET, Abdelazeem MA, Yaser HA. The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods. 2020; 9: 374.
2. Rauf A, Imran M, Khan IA, Ur-Rehman M, Gilani SA, Mehmood Z, Mubarak MS. Anticancer Potential of Quercetin: A Comprehensive Review. Phytother Res. 2018; 32: 2109–2130.
3. Yuanyuan D, Chaomei L, Yongjing Z, Pengyu M, Tingting Z, Delu C, Jiao C, Jue W, Rui L, Tao Z, Langchong H. Quercetin as a Lyn Kinase Inhibitor Inhibits IgE-Mediated Allergic Conjunctivitis. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020; 135: 110924.
4. Zhanxin Y, Yeqing G, Qing Z, Li L, Ge M, Hongmei W, Yang X, Xue B, Hongbin S, Shaomei S, Xing W, Ming Z, Qiyu J, Yuntang W, Kun S, Weina G, Changjiang G, Kaijun N. Estimated Daily Quercetin Intake and Association with the Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Adults. Eur J Nutr. 2019; 58: 819–830.
5. Perdicaro DJ, Rodriguez Lanzi C, Gambarte Tudela J, Miatello RM, Oteiza PI, Vazquez Prieto MA. Quercetin Attenuates Adipose Hypertrophy, in Part through Activation of Adipogenesis in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet. J Nutr Biochem. 2020; 79: 108352.
6. Nutmakul T. A Review on Benefits of Quercetin in Hyperuricemia and Gouty Arthritis. Saudi Pharm J. 2022; 30: 918–926.
7. Yue L, Zhen-Gang T, Yi L , Xin-Guo Q, Wei L, Guo-Bin W, Cai-Li L. Effects of Quercetin on Proliferation and Migration of Human Glioblastoma U251 Cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017; 92: 33–38.
8. Klara Z, Vedrana R , Josipa V, Patrick R, Nada O, Goran Š, Maja J. PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling are involved in quercetin-mediated neuroprotection against copper-induced injury Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; Article ID 9834742.
9. Xu. D, Hu. M.J, Wang. Y.Q, Cui. Y.L. Antioxidant activities of quercetin and its complexes for medicinal application Molecules. 2019; 24: 1123
10. Kuo SM, Huang CT, Blum P, Chang C. Quercetin cumulatively enhances copper induction of metallothionein in intestinal cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2001; 84: 1-10.
11. Hai Y, Zhang Y, Liang Y, Ma X, Qi X , Xiao J, Xue W, Luo Y, Yue T. Advance on the absorption, metabolism and efficacy exertion of quercetin and its important derivatives. Food Front. 2020; 1: 420-434.
12. Norden DM, Trojanowski PJ, Villanueva E, Navarro E, Godbout JP. Sequential activation of microglia and astrocyte cytokine expression precedes increased Iba-1 or GFAP immunoreactivity following systemic immune challenge. Glia. 2016; 64: 300–316.
13. Liya Q, Xuefei W, Michelle LB, Yuxin L, George RB, Jau-Shyong H, Darin JK, Fulton TC. Systemic LPS causes of chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Gila. 2007; 55(5): 453-462.
14. Boots AW, Haenen GR, Bast A. Health Effects of Quercetin: From Antioxidant to Nutraceutical. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008; 585: 325–337.
15. Cao Y, Zhao H, Wang Z, Zhang C, Bian Y, Liu X, Zhang C, Zhang X, Zhao Y. Quercetin Promotes in Vitro Maturation of Oocytes from Humans and Aged Mice. Cell Death Dis. 2020; 11: 965.
16. Ezzati M, Yousefi B, Velaei K, Safa A. A Review on Anti-Cancer Properties of Quercetin in Breast Cancer. Life Sci. 2020; 248: 117463.
17. Sánchez-González PD, López-Hernández FJ, Dueñas M, Prieto M, Sánchez-López E, Thomale J, Ruiz-Ortega M, López-Novoa JM, Morales AI. Differential Effect of Quercetin on Cisplatin-Induced Toxicity in Kidney and Tumor Tissues. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017; 107: 226–236.
18. Edwards RL, Lyon T, Litwin SE, Rabovsky A, Symons JD, Jalili T. Quercetin Reduces Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Subjects. J Nutr. 2007; 137: 2405–2411.
19. Singh V, Chauhan G, Shri R. Anti-Depressant like Effects of Quercetin 4’-O-Glucoside from Allium Cepa via Regulation of Brain Oxidative Stress and Monoamine Levels in Mice Subjected to Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress. Nutr Neurosci. 2019; 24: 35–44.
20. Fidler Y, Gomes J. Effects of a single dose of X-ray irradiation on MMP-9 expression and morphology of the cerebellum cortex of adult rats. Cerebellum 2023; 22(2): 240–248.
21. Kobayashi S, Saio M, Fukuda T, Kimura K, Hirato J, Oyama T. Image analysis of the nuclear characteristics of emerin protein and the correlation with nuclear grooves and intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2019; 41:133–142.
22. Fatemeh A, Milad H. Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7): 1020.
23. Kalinowska K, Chen J, Dresselhaus T. Imaging of embryo sac and early seed development in maize after Feulgen staining. Methods Mol Biol. 2020; 2122: 191–203.
24. Van Bregt DR, Thomas TC, Hinzman JM, Cao T, Liu M, Bing G, Gerhardt GA, Pauly JR, LIfshitz J. Substantia nigra vulnerability after a single moderate diffuse brain injury in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2012; 233(1): 282-292.
25. Burk RF, Hill KE, Motley AK, Winfrey VP, Kurokawa S, Mitchell SL, Zhang W, Torano JS, Birringer M, Saito Y, Takahashi K. Combined deficiency of vitamins E and C causes severe central nervous system damage in guinea pigs. J Nutr. 2006; 136(10): 2540-2545.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.




